The parent compound of rifamycin was rifamycin B which was originally obtained as a main product in the presence of diethylbarburitic acid Some small modifications where performed in this inactive compound and with the creation of rifamycin SV there was the first antibiotic used intravenously for the treatment of tuberculosis 2Rifamycins Mode of action Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis Enters neutrophils and macrophages and inhibits DNAdependent RNA polymerase in bacteria Example Rifampin, Rifabutin, Rifapentine Source Amycolaptosis mediterrainei Spectrum of activityRifamycin antibiotics, like rifampin and rifapentine, have unique sterilizing activity against Onethird of the world's population is infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) can progress to tuberculosis disease, the leading cause of

Konjungtivitis Bayi Usia 14 Bulan Apa Yang Harus Dilakukan
Rifamycine pommade bébé
Rifamycine pommade bébé-The rifamycins are a group of antibiotics that are synthesized either naturally by the bacterium Amycolatopsis rifamycinica or artificially They are a subclRifampicin is an immunosuppressive agent For a safer, and easier to use Rifampicin, try TOKUE's readymade Rifampicin Solution (10 mg/mL in water) Synonyms RFP, Rifampin, 3 ( ( (4Methyl1piperazinyl)imino)methyl)rifamycin SV, NIH 107, NSC Mechanism of Action Rifampicin targets prokaryotic DNA dependent RNA polymerases which




Calameo Prendre Soin De L Enfant De 3 Mois A 3 Ans
H410 (50%) Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, longterm hazard Precautionary Statement Codes P260, P264, P270, P273, P301P312, P309P311, P330, P391, P405, and P501 (The corresponding statement to each Pcode can be found at the GHS Classification page)Rifamycin S is a quinone and an antibiotic agnet against Grampositive bacteria (including MRSA) Rifamycin S is the oxidized forms of a reversible oxidationreduction system involving two electrons Rifamycin S generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits microsomal lipid peroxidation Rifamycin S can be used for tuberculosis and leprosy Find everything you need to know about Rifampin (Rifadin), including what it is used for, warnings, reviews, side effects, and interactions Learn more about Rifampin (Rifadin) at EverydayHealthcom
This medication is a rifamycin antibiotic used to prevent and treat tuberculosis and other infectionsThis antibiotic treats only bacterial infectionsIt will not work for viral infections (such loss of appetite lower back or side pain mental depression nausea painful or difficult urination persistent bleeding or oozing from puncture sites, mouth, or nose puffiness or swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes, face, lips, or tongue skin itching, rash, or redness sores, ulcers, or white spots on the lips or in the mouthLe collyre antibiotique AZYTER ( azithromycine ) peut être utilisé dès la naissance dans le traitement curatif local antibactérien des conjonctivites dues à des germes sensibles Le collyre antibiotique AZYTER 15 mg/g en récipients
Rifamycin B ( CHEBI ) is a carboxylic acid ( CHEBI ) rifamycin B ( CHEBI ) is a organic heterotetracyclic compound ( CHEBI ) rifamycin B ( CHEBI ) is a rifamycins ( CHEBI ) rifamycin B ( CHEBI ) is conjugate acid of rifamycin BRifamycin S MFCD MDL number Predicted ACD/Labs;Dans ce cas, votre bébé a besoin d'un traitement antibiotique Quel collyre antibiotique pour bébé?




My Life My World My Microbe La Boite A Pharmacie



Sante Bebe Bebesante Fr Page 6
The four rifamycins approved for clinical use, rifampicin, rifabutin, rifapentine, and rifaximin (), are available as orally formulated agents derived from rifamycin SV, the natural product of Amycolatopsis mediterranei (alias Streptomyces mediterranei) (Tupin et al 10)The rifamycins are transcriptional inhibitors, and bind specifically to the β subunit of RNA polymerases from aRifamycin is used to treat of travelers' diarrhea caused by certain bacteria Rifamycin is in a class of medications called antibiotics It works by stopping the growth of the bacteria that cause diarrhea Antibiotics such as rifamycin will not work for colds, flu, or other viral infections RIFAMYCINE CHIBRET posologie découvrez les indications, pour grossesse, femme enceinte, bébé, enfant, alcool ainsi que l'avis d'un expert !




Collyre Antiseptique Collyre Sans Ordonnance Contre Les Yeux Rouges




Collyres Des Effets Secondaires Dangereux Pour Les Enfants Top Sante
Din, Rimactane) is an oral antibiotic used to prevent and treat tuberculosis ( TB) and other bacterial infections Side effects of rifampin include headache, drowsiness, dizziness, harmless discoloration of body fluids, and others Learn more about the side effects, uses, dosage, and pregnancy safety information for this antibioticRifamycin is used to treat diarrhea caused by the common bacteria known as E coli ("traveler's diarrhea") It works by stopping the growth of bacteriaThis antibiotic treats only bacterialRifaximin is a derivative of rifamycin that is poorly absorbed after oral administration;




Incidence Et Facteurs De Risque Des Conjonctivites Chez Les Nouveau Nes Traites Par Rifamycine Collyre En Prophylaxie Au Centre Hospitalier Universitaire D Amiens Du 1er Septembre 15 Au 4 Janvier 16 Semantic Scholar




Conjonctivite Traitement Comment La Soigner Correctement
Rifampicin is of the rifamycin group of antibiotics It works by decreasing the production of RNA by bacteria Rifampicin was discovered in 1965, marketed in Italy in 1968, and approved in the United States in 1971 It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential MedicinesRifampicin An antibiotic drug used mainly to treat TUBERCULOSIS and LEPROSY, but also LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE, PROSTATITIS, ENDOCARDITIS and OSTEOMYELITIS Rifampicin acts by inhibiting transcription of bacterial nucleic acid It interferes with the action of oral contraceptivesBrief Overview of the Antibiotic Known as Rifampin!!Check us out on Facebook for DAILY FREE REVIEW QUESTIONS and updates!
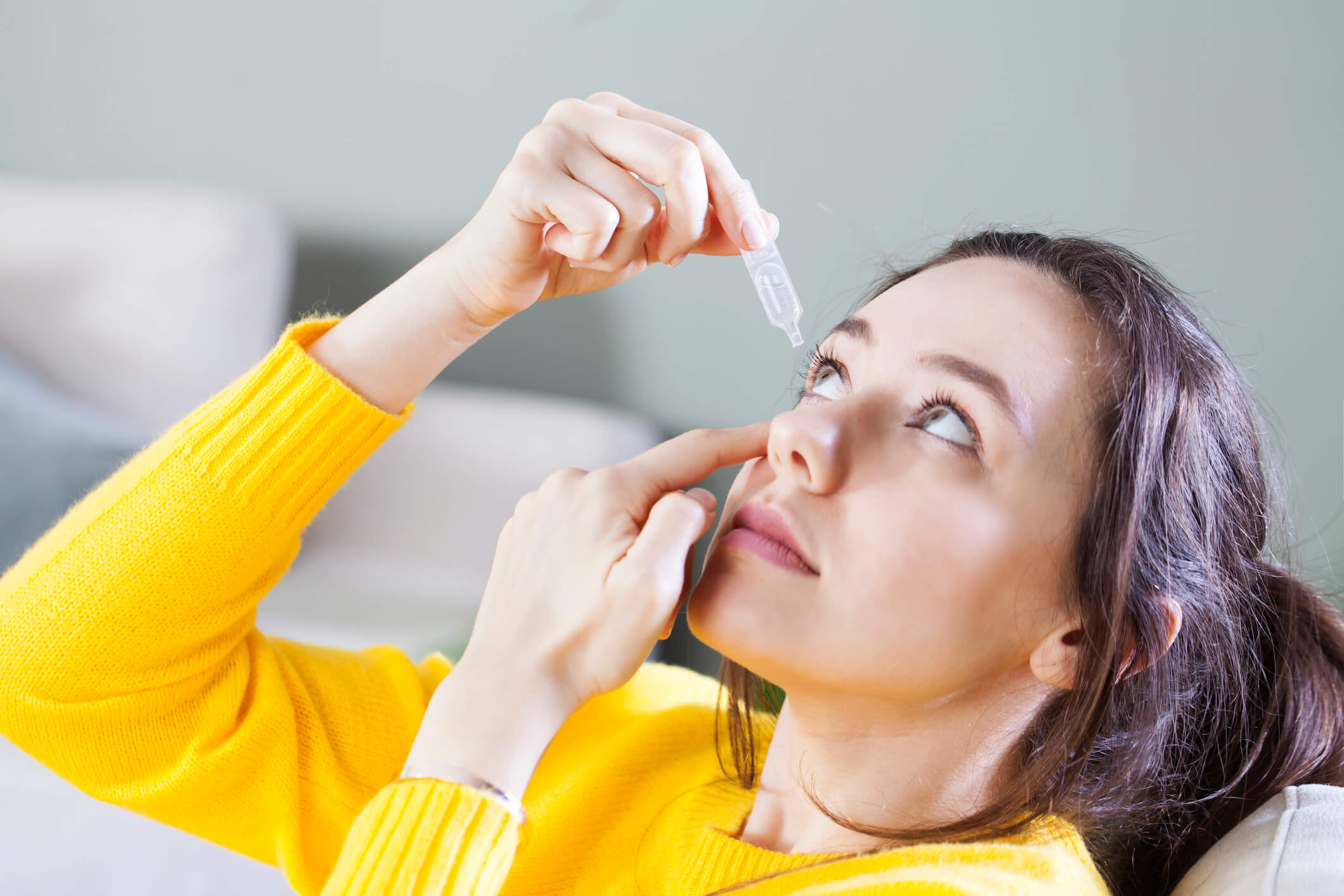




Conjonctivite Traitement Comment La Soigner Correctement




Babibop Fr Soins Bebe Nourisson Comment Nettoyer Les Yeux De Bebe Youtube
Literature References Group of antibiotics characterized by a natural ansa structure (chromophoric naphthohydroquinone group spanned by a long aliphatic bridge) not previously found in other known antibiotics Isoln from the fermentation broths of Streptomyces mediterranei P Sensi et al, Antibiot Annu , 262 Among rifamycins, rifamycin B, O, S, SV and X are the morePredicted data is generated using the ACD/Labs Percepta Platform PhysChem Module Density 13±01 g/cm 3 Boiling Point 9174±650 °C at 760 mmHg Vapour Pressure 00±03 mmHg atRifamycin B is a carboxylic acid, an acetate ester, an organic heterotetracyclic compound and a member of rifamycins It is a conjugate acid of a rifamycin B(2)




Laccouchement Definitions Accouchement Ensemble Des Phnomnes Mcaniques Il




La Prevention De La Conjonctivite Chez Le Nouveau Ne Soins De Nos Enfants
The diethylamide of rifamycin B (commonly known as rif amide, XII, Table 1) was synthesized in 1963 and used in therapeutic treat ment under the trademark Rifocin M (30) The rifamycins were isolated by Sensi and colleagues at the DowLepetit Research Laboratories in Milan in 1959 as a mixture of five substances from fermentation cultures of the organism now classified as Amycolatopsis mediterranei, which belongs to the Actinomycetaceae Nicknamed "Rififi" after a French crime movie, the official name became rifamycin 1 Rifamycin SV, the first rifamycinRifampin is usually well tolerated and produces few adverse effects GI disturbances and abnormalities in liver function (icterus) have been reported in people Hypersensitivity reactions can also result from rifampin administration, and renal failure is a possible consequence when intermittent dosage schedules are followed Partial, reversible immunosuppression of




Conjonctivite Et Bronchite Journal D Une Naturopathe




Bebe A Le Canal Lacrymal Bouche Guerir Ces Yeux Qui Pleurent Reflex Osteo
Like all medicines, RIFAMYCINE CHIBRET® 1 000 000 UI PERCENT, eye drops in solution, can involve side effects Possible transient irritations, risk of allergic reactions, because of the presence of potassium metabisulfite, risk of allergicAll the therapeutically useful rifamycins are semisynthetic derivatives of rifamycin B, a fermentation product that is poorly active, but easily produced and readily converted chemically into rifamycin S, from which most active derivatives are prepared They all share the general structureRifamycin is used in adults to treat traveler's diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli (E coli) Rifamycin is not for use in treating diarrhea with fever or blood in the stools, or diarrhea that is not caused by E coli Rifamycin may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide




Incidence Et Facteurs De Risque Des Conjonctivites Chez Les Nouveau Nes Traites Par Rifamycine Collyre En Prophylaxie Au Centre Hospitalier Universitaire D Amiens Du 1er Septembre 15 Au 4 Janvier 16 Semantic Scholar




Acne Du Nourrisson Causes Et Remedes
Rifamycin SV MMX ® is a pharmaceutical product employing rifamycin SV engineered with the MMX ® technology Rifamycin SV is a broad spectrum, semisynthetic, orally nonabsorbable antibiotic which can be used for the treatment of bacterial infections of the colon such as traveler's diarrhea, infectious colitis, Clostridium difficile associated disease, diverticulitis and also asJames Staunton, Barrie Wilkinson, in Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry, 1999 Precursor Studies Evidence for the processive mechanism of rifamycin B biosynthesis was first observed through the accumulation of a "tetraketide" chain elongation intermediate P8/1OG (54) from a mutant of A mediterranei 114 This evidence and the demonstration from feedingPrice based on 550mg, 42 tablets (generic if available) See Prices Rifadin (rifampin) Drug class Rifamycins RIFAMPIN is an antibiotic It is used to treat or prevent certain kinds of bacterial infections It is used to treat or prevent tuberculosis (TB) It



Rifamycine Chibret 1 000 000 Ui 100ml Colly En Sol Fl 10ml Pharmnet Encyclopedie Des Medicaments En Algerie Propriete Sarl Esahti



Tobracol Les Laboratoires Unimed
This rifamycin derivative is not effective, however, as monotherapy for existing disseminated MAC disease Rifabutin is a very lipophilic compound with a high affinity for tissues Its elimination is distribution limited, with a halflife averaging 45 hours (range, 1669 hours) Approximately 50% of an orally administered dose of rifabutin isRifampin specifically inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase, the enzyme responsible for DNA transcription, by forming a stable drugenzyme complex with a binding constant of 10(9) M at 37 C The corresponding mammalian enzymes are not affected by rifampin Bacterial resistance to rifampin is caused by Rifampin USP, is a semisynthetic antibiotic derivative of rifamycin B, available as 300mg capsules for oral administration Rifampin is 3 (4 methyl1piperazinyl) imino methyl rifamycin, and its structural formula is Rifampin USP is a redbrown crystalline powder It is very slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in chloroform, and




Tuberculosis Treatment French Symposia The Crudem Foundation



Static Cnsf Asso Fr Wp Content Uploads 18 04 Livret Sf Et N Ne V5 29 9 11 h30 Pdf
97% is recovered primarily unchanged in feces Rifaximin can be used for empiric treatment of Traveler's diarrhea , which is caused primarily by enterotoxigenic and enteroaggregative Escherichia coli rifamycin SV ChEBI ID CHEBI Definition A member of the class of rifamycins that exhibits antibiotic and antitubercular properties Stars This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team Supplier Information We are unable to retrieve the vendor information for this entry at this timeA rifamycinbased nonsystemic antibiotic used for the treatment of gastrointestinal bacterial infections, such as traveler's diarrhea and irritable bowel syndrome, and reduction of overt hepatic encephalopathy recurrence in adults Rifamycin An antibacterial used to treat traveler's diarrhea 25desacetylrifapentine




5 Conseils Pour Soigner La Conjonctivite De Bebe Neufmois Fr




Calameo Prendre Soin De L Enfant De 3 Mois A 3 Ans
N'utilisez jamais RIFAMYCINE CHIBRET 1000 000 UI POUR CENT, collyre en solution si vous êtes allergique à l'un des constituants du collyre, notamment à la rifamycine Faites attention avec RIFAMYCINE CHIBRET 1000 000 UI POUR CENT, collyre en solution Ne pas injecter, ne pas avaler Informez votre médecin si vous avez uneRifampin is usually well tolerated and produces few adverse effects GI disturbances and abnormalities in liver function (icterus) have been reported in people Hypersensitivity reactions can also result from rifampin administration, and renal failure is a possible consequence when intermittent dosage schedules are followed Partial, reversible immunosuppression ofRifamycin B European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard Synonym Rifamycin impurity A CAS Number Empirical Formula (Hill Notation) C 39 H 49 NO 14 Molecular Weight Beilstein/REAXYS Number NACRES N4




10 Astuces Pour Enlever Les Taches De Bebe Magicmaman Com
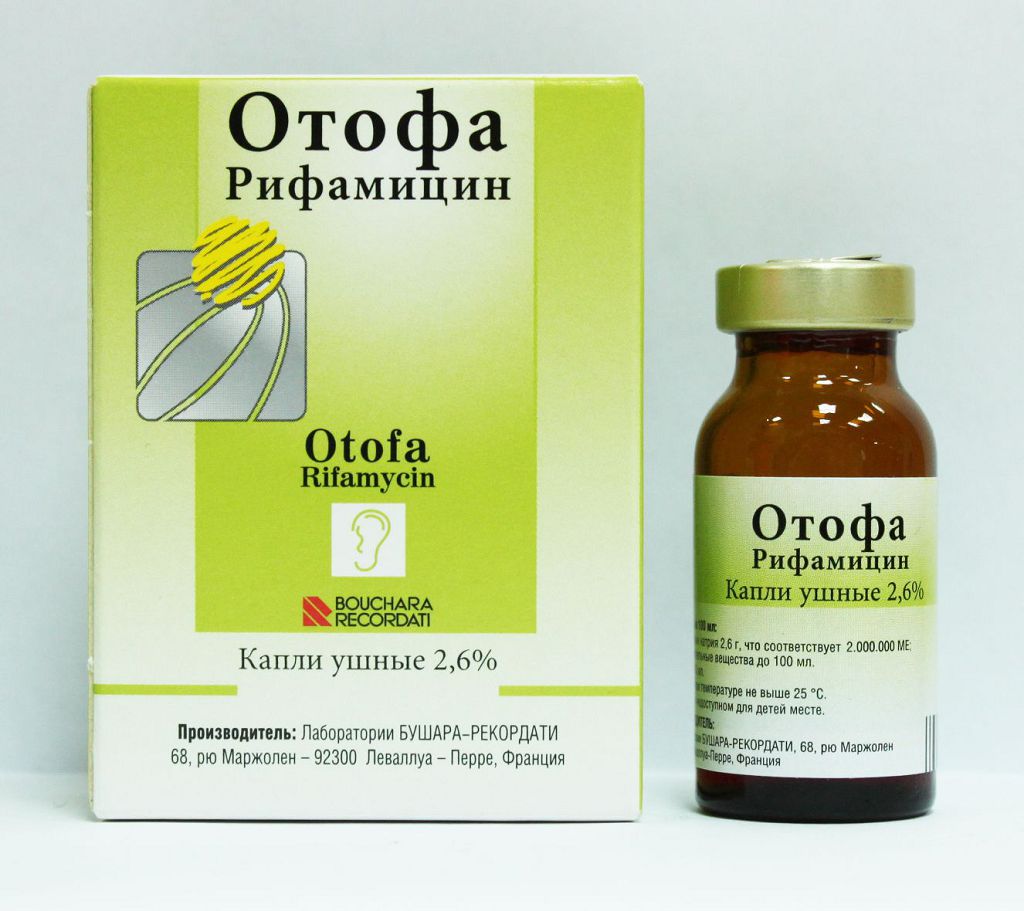



Otofa Pour Les Enfants Mode D Emploi Des Gouttes Auriculaires Des Critiques Comparaison Avec Otypaks Qui Est Mieux
MCUL Molport MolPort NIAID Royal Society of Chemistry rifamycin B Springer Nature Biological conversion of rifamycin B by live Humicola sp cells immobilized in a dual hollow fiber bioreactor, A strain ofNocardianmediterranei that produces a mixture of rifamycin B and W, Microbial transformation ofAmong these, rifamycin B isolated in a pure form Although its antimicrobial activity was moderate, it was oxidized and hydrolyzed to yield the highly active rifamycin S, a quinone molecular with potent antimicrobial activity but poor tolerabilityAbstract Five actinophages highly specific for Streptomyces mediterranei were isolated from lysed broth cultures Studies were performed on the effect of plating conditions on plaque formation The development of phageresistant strains of S mediterranei not only eliminated the phage but also significantly increased rifamycin yields The phageresistant cultures proved to be more




Medicaments




Les Collyres Peuvent Etre Dangereux Pour Les Yeux Des Plus Petits Lci




Mon Bout Chou A Mal Bebe Grandit Forum Grossesse Amp Bebe Doctissimo
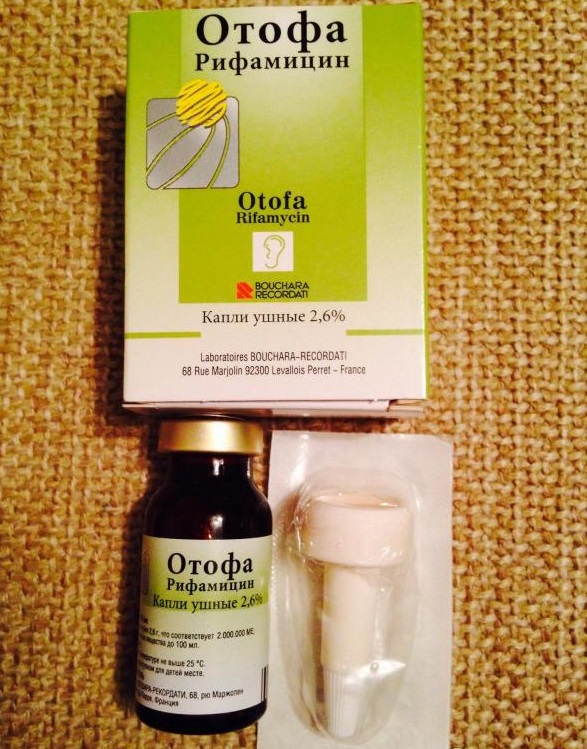



Otofa Pour Les Enfants Mode D Emploi Des Gouttes Auriculaires Des Critiques Comparaison Avec Otypaks Qui Est Mieux



La Promethazine Mort Subite De L Enfant Pharamster Un Regard Officinal Independant Sur Les Medicaments




Plus De Gouttes Dans Les Yeux Du Nouveau Ne Destination Sante



Dumas Ccsd Cnrs Fr Dumas Document




Prise En Charge Nouveau Ne En Salle De Naissance Soins D Yeux Pdf Free Download




Dacryocystoceles Congenitales Traitement Chirurgical Ou Simple Surveillance Sciencedirect




Incidence Et Facteurs De Risque Des Conjonctivites Chez Les Nouveau Nes Traites Par Rifamycine Collyre En Prophylaxie Au Centre Hospitalier Universitaire D Amiens Du 1er Septembre 15 Au 4 Janvier 16 Semantic Scholar



Blog Grossesse Elise Et Antoine Accouchement Prevu Le 8 Novembre 12




Rifamycine Colly 1 Fl10ml



Notice Patient Otofa Solution Auriculaire En Gouttes Base De Donnees Publique Des Medicaments



Http Www Cpias Auvergnerhonealpes Fr Reseaux Mater Journee 13 6 Desinfection Oculaire Pdf




Conjonctivite Bebe Comment La Reconnaitre Et La Traiter La Bonne Vue



L œil Qui Coule Bebesante Fr




Rp N 176 By Performances Medicales Issuu




Calameo Le Manuel Des Gardes Pediatrie
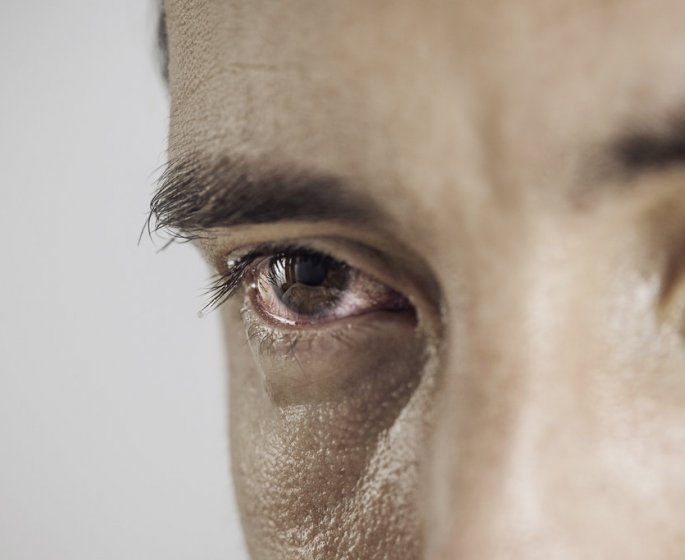




Conjonctivite Symptomes Contagion Traitements Duree Medisite




La Conjonctivite Du Nourrisson Magicmaman Com




Compendium Ch




Calameo Livre Guide D Utilisation Des Medicaments3




Rifamycines Medqual



Http Www Spo Dz Com Website Events Files 42 Les urgences ophtalmo P C3 diatriques le m C3 decin g C3 n C3 raliste E2 80 A6 Premier maillon de l E2 80 99urgence Pdf



Revue De Sante Oculaire Communautaire Comment Instiller Un Collyre Ou Appliquer Une Pommade Oculaire Dans Les Yeux D Un Nourrisson Ou D Un Jeune Enfant



Www Jbhsante Com File Download Assets bd29ad01b94b57abe1df2a85cf7f36ee91a Pdf Ro125



Pivalone Pharmabolix




Prophylaxie Des Infections Conjonctivales Du Nouveau Ne
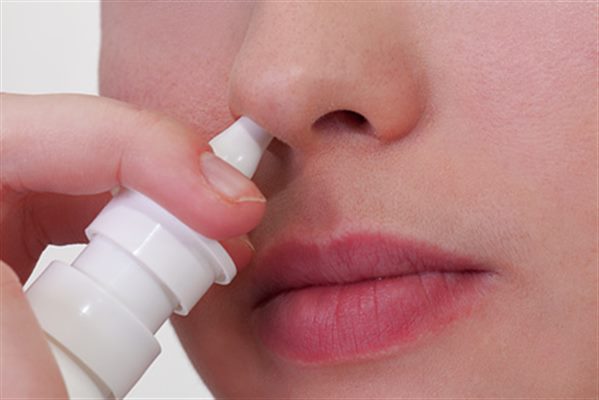




Gouttes Dans Le Nez Definition Docteurclic Com




Conjonctivites Du Nouveau Ne Et Du Nourrisson Sciencedirect




Bebe Conjonctivites Repetitives Canal Lacrymal Bouche Les Aventures Du Chouchou Cendre




La Conjonctivite Du Nourrisson Magicmaman Com




Ses Yeux Coulent Conjonctivite La Maison Des Maternelles Lmdm Youtube




Conjonctivite Et Bronchite Journal D Une Naturopathe




Conjonctivite Du Bebe Que Faire Quels Traitements Top Sante



Www Cahiers Ophtalmologie Fr Media 7b2db5be594f9a3fe1849f Pdf




Mon Officine A Moi Home Facebook



Http Www Reseauperinatmed Fr Collyre Salle Naissance Nicolas Falaise 171 Html




Collyres En Ophtalmologie Ppt Telecharger




Conjonctivite Et Inflammation De L Oeil




Konjungtivitis Bayi Usia 14 Bulan Apa Yang Harus Dilakukan




Oroken Avis




Pdf Ectropion Congenital Bilateral Avec Important Chemosis




Collyres En Ophtalmologie Ppt Telecharger




Pediatrie Douleur Enfant Premature




Conjonctivite Neonatale Pediatrie Edition Professionnelle Du Manuel Msd



Ces Soins Que Bebe Recevra A La Naissance Monpremierbebe Fr
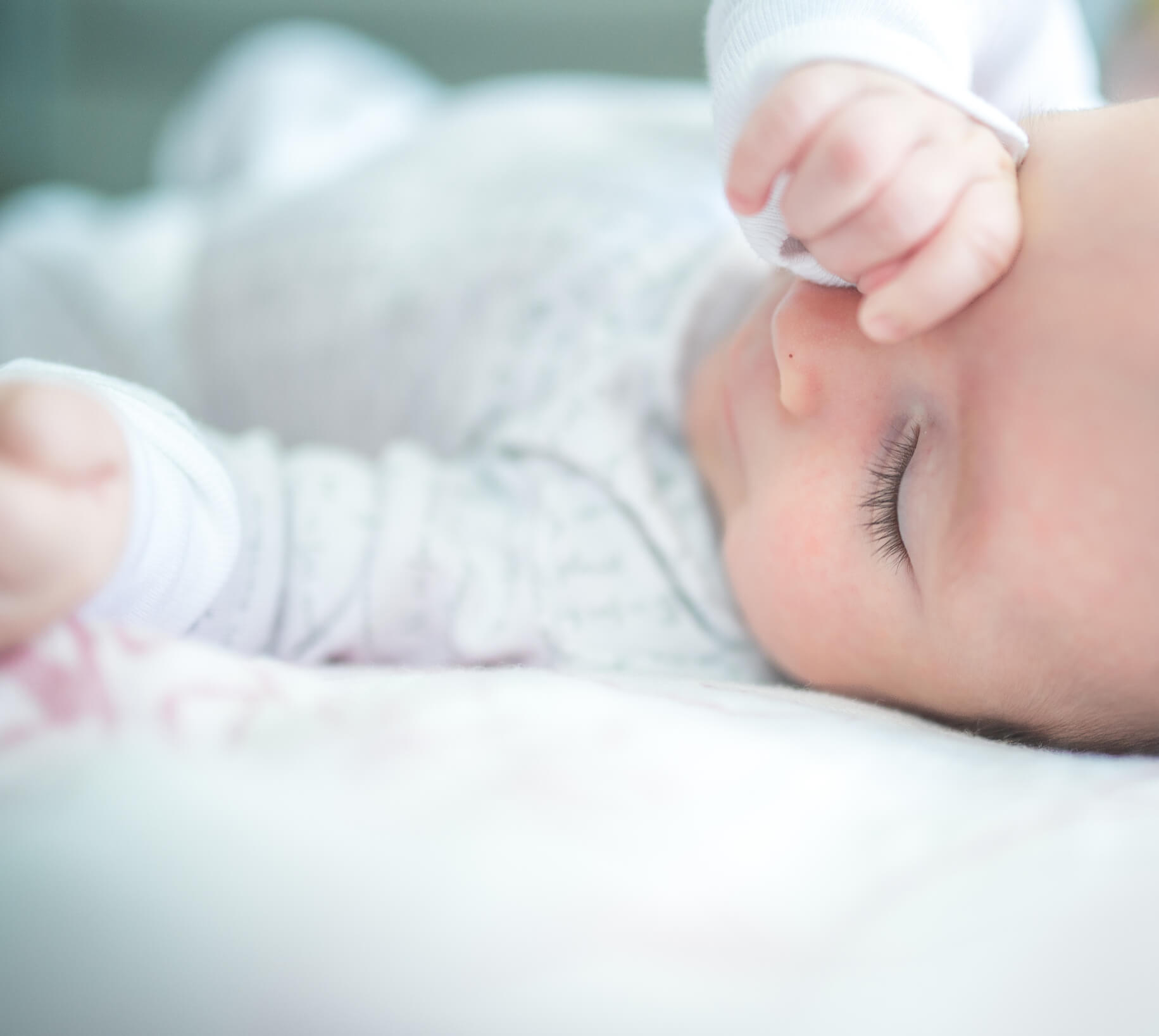




Conjonctivite Bebe Nos Conseils Pour Bien La Soigner



L œil Qui Coule Bebesante Fr




Le Chalazion Pharmacien Giphar



L œil Qui Coule Bebesante Fr




La Conjonctivite Doctissimo



Http Www Realites Pediatriques Com Wp Content Uploads 16 05 Rp 171 Dos Sauer 1 Pdf



Ingestion Erronee De Medicaments Bebes Et Mamans




Bebe Sous Antibiotiques Attention A La Diarrhee Et A La Deshydratation Laboratoire Pediact
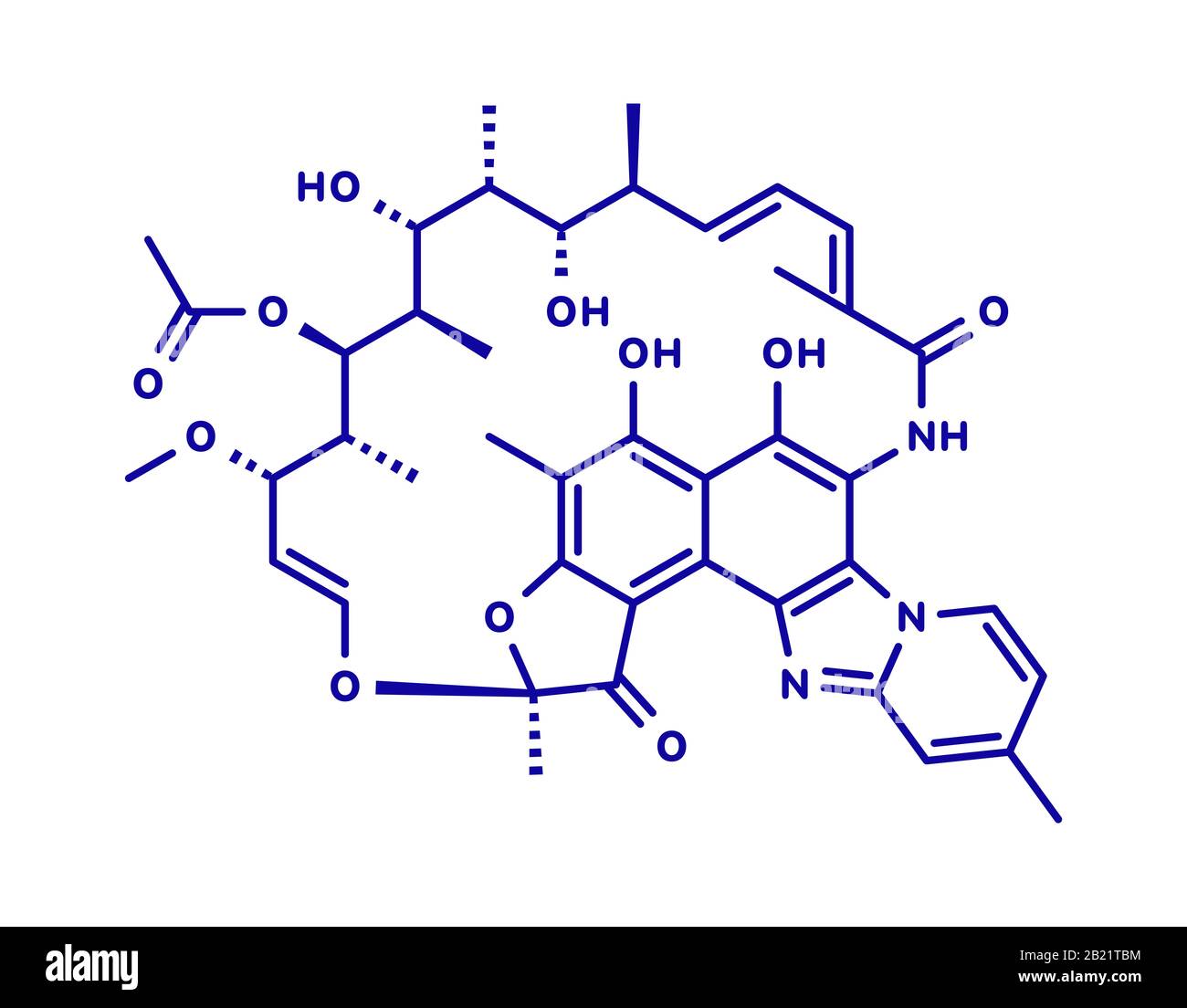



Rifamycine Banque D Image Et Photos Alamy



Bebe Conjonctivites Repetitives Canal Lacrymal Bouche Les Aventures Du Chouchou Cendre



L Afssaps Interdit Les Mucolytiques Chez Les Moins De 2 Ans Pharamster Un Regard Officinal Independant Sur Les Medicaments
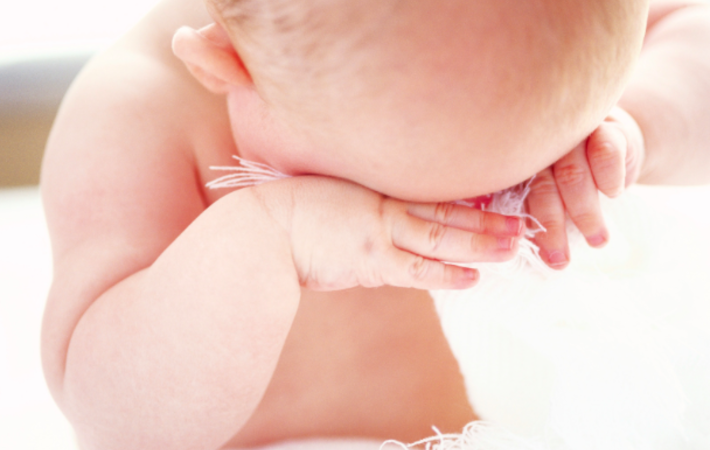




Bebe A Le Canal Lacrymal Bouche Guerir Ces Yeux Qui Pleurent Reflex Osteo



Http Www Afsop Fr Wp Content Uploads Documents Officiels Map Infections Conjonctivales Nouveaune Pdf




Prophylaxie Des Infections Conjonctivales Du Nouveau Ne



Blog Grossesse Elise Et Antoine Accouchement Prevu Le 8 Novembre 12
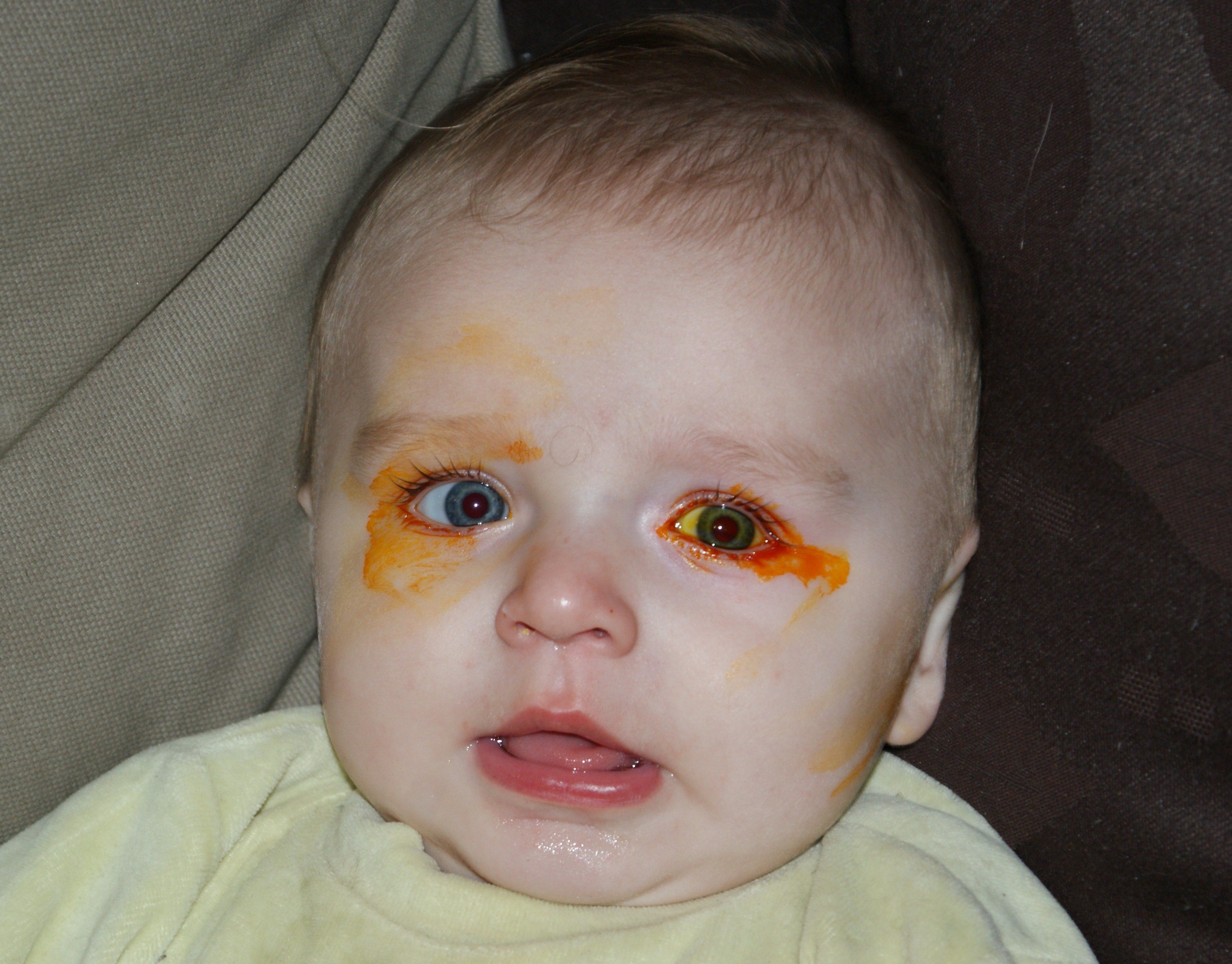



Yeux Colles Bebe Grandit Forum Grossesse Amp Bebe Doctissimo



Prophylaxie Des Infections Conjonctivales Du Nouveau Ne Reseau Perinatalite De Franche Comte




Conjonctivite Comment La Reconnaitre Et La Traiter




Les Collyres Dangereux Pour Les Bebes Top Sante



Static Cnsf Asso Fr Wp Content Uploads 18 04 Livret Sf Et N Ne V5 29 9 11 h30 Pdf



Rapport Sfo 17 Ophtalmologie Pediatrique




Incidence Et Facteurs De Risque Des Conjonctivites Chez Les Nouveau Nes Traites Par Rifamycine Collyre En Prophylaxie Au Centre Hospitalier Universitaire D Amiens Du 1er Septembre 15 Au 4 Janvier 16 Semantic Scholar
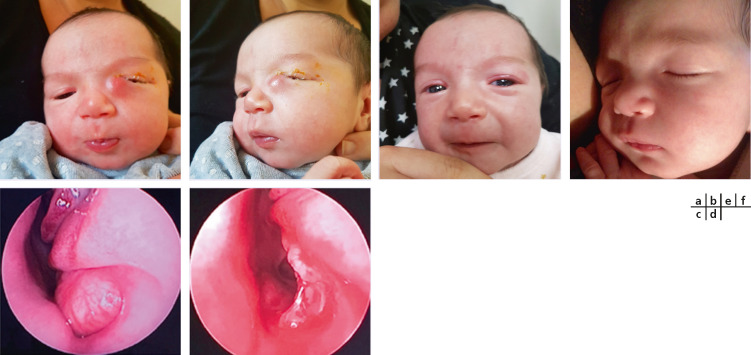



Rapport Sfo 17 Ophtalmologie Pediatrique




11 Ophtalmologie Medicine Key
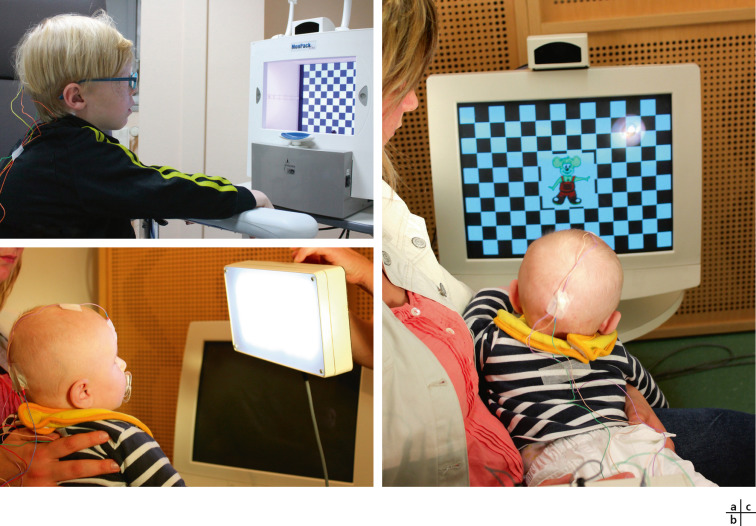




Rapport Sfo 17 Ophtalmologie Pediatrique




Le Coin Du Prescripteur




La Conjonctivite Chez Bebe Un Traitement Simple A Appliquer Babyfrance Com




Incidence Et Facteurs De Risque Des Conjonctivites Chez Les Nouveau Nes Traites Par Rifamycine Collyre En Prophylaxie Au Centre Hospitalier Universitaire D Amiens Du 1er Septembre 15 Au 4 Janvier 16 Semantic Scholar




Conjonctivite Et Bronchite Journal D Une Naturopathe



Http Www Reseauperinatmed Fr Collyre Salle Naissance Nicolas Falaise 171 Html
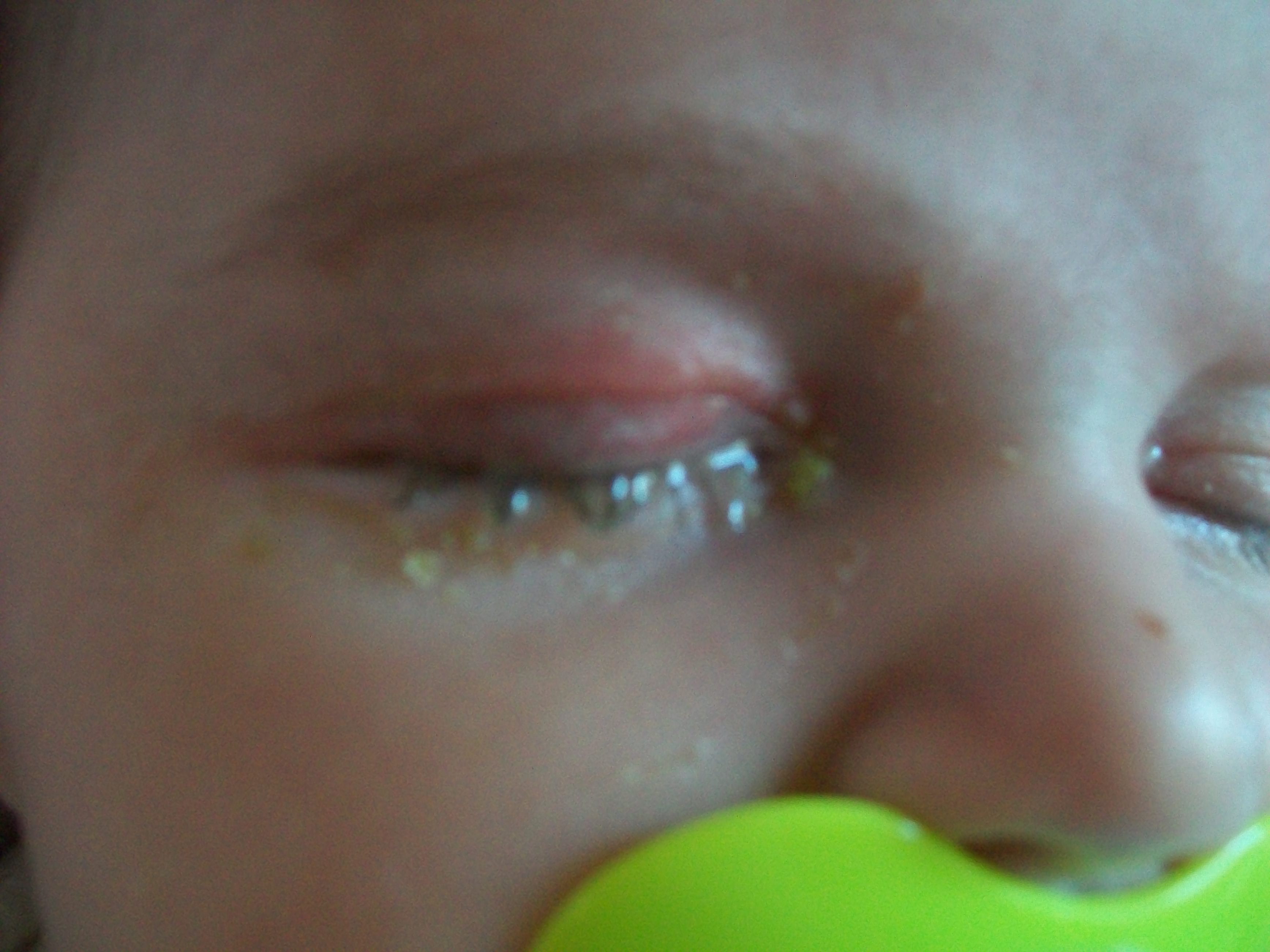



Canal Lacrymal Bouche Bebe Grandit Forum Grossesse Amp Bebe Doctissimo


